Read on, we cover hybrid cloud security solutions necessary to protect digital assets in these environments. This includes fundamental elements such as data encryption, network security and identity management and the top things to do when you secure hybrid clouds. Whether you use public, private or multi-cloud environments, this guide gives you the strategies to secure your datas and maintain compliance across platforms.
The rise of hybrid cloud environments driven by evolving digital use cases makes securing assets a tough nut to crack for many organizations. Hybrid clouds — These cloud environments give businesses the elasticity of public clouds with the greater degree of management and security provided by private clouds, thus enabling a hybrid infrastructure that spans an on-premises data center to private-cloud hosted resources up to third-party public cloud. While this combination provides many benefits, it also poses a number of specific security threats. In this guide, we highlight several security practices you should consider to lock down your hybrid cloud.
The Rise of Hybrid Cloud Environment

In the meantime, hybrid cloud environments have become the chief approach for many companies that are looking to balance cost and flexibility with control. In this hybrid cloud model, customers can scale applications and data across private clouds for highly sensitive ones whilst scaling up or down to the public when needed. Integration of multiple cloud providers (Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, AWS etc) allow organizations to cherry pick the service and pricing model based on their use case.
But how does the security of data become complicated in hybrid environments, even though these are all under one roof — disparate and unique from each other for sure—but now too complex to be guarded against if they happen hosts need changes everywhere because a single provider has shared responsibilities model. This complexity also highlights the need for a security architecture that enables consistent policies across hybrid cloud environments and ensures security coverage throughout.
Core Hybrid Cloud Concepts
- Hybrid cloud: A mix of on-premises infrastructure and one or more public and private clouds.
- Hybrid cloud architecture: The makeup of a hybrid cloud, such as how different components connect and manage one another.
- Hybrid cloud infrastructure: Hardware, software and networking resources (IaaS) which support hybrid cloud operation.
- Multi-cloud: The concept of using multiple public cloud platforms in a common environment is called Multi-Cloud.
Features Of Hybrid Clouds
- Flexibility and scalability: Ease of moving workloads between public or private clouds for changes in business requirements.
- Improved cost efficiency: Use public clouds to gain the price advantage for non-critical workloads while keeping sensitive data in private cloud environments.
- Data residency and sovereignty: Maintaining compliance while storing particularly sensitive data only in geographical regions meeting specific regulatory requirements.
- Complexity: Managing diverse infrastructure, applications, and data across multiple cloud platforms and on-premises environments.
Hybrid Cloud Security Challenges
Securing hybrid cloud environments presents significant hurdles:
- Data privacy and compliance: Protecting sensitive data while adhering to industry regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Visibility and control: Maintaining a comprehensive view of security posture across public clouds, private clouds on-premises infrastructure.
- Use case: Threat detection and response—detecting ransomware, phishing attacks, DDoS etc., in a complex dynamic landscape.
- Lack of security skills: Recruiting and retaining experienced cloud normalization and on-premises safety specialists.
Understanding these hybrid cloud security challenges helps companies build effective strategies to secure their digital assets.
Fundamental Hybrid Cloud Security Solutions
To effectively protect your hybrid cloud environment, a combination of security solutions is essential.
Zero Trust Architecture
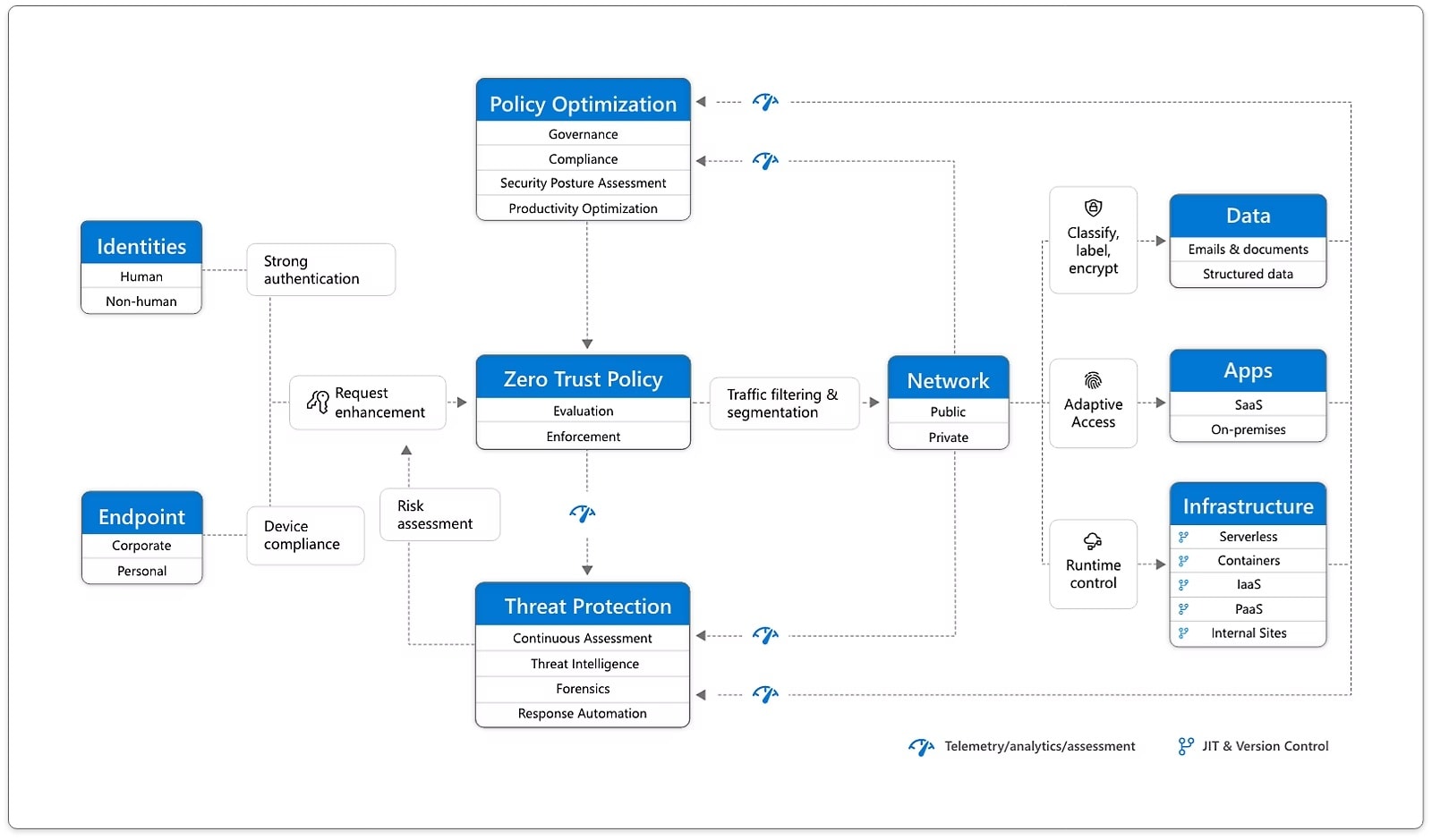
Historically, security models were based on the assumption that everything inside a corporate network could be trusted. On the other hand, a Zero Trust model subscribes to “never trust, always verify”. This method squirms the normal boundary of a network and enforces that every access request be authenticated regardless face to screen or not.
Zero Trust operates on the assumption of a breach, because it puts authentication, authorization and encryption into high gear. It provides least privilege access, enforcing the idea of granting permissions to a user only what is absolutely necessary. Finally, microsegmentation is capable of securing isolated network “segments” in order to provide threat containment options for critical-to-service applications and their workloads. Anomalies are detected using advanced analytics and threat intelligence, which triggers an incident.
This hybrid cloud security model is essential to protect today’s organizations that increasingly depend on remote work, cloud services, and intricate IT infrastructures. Businesses can greatly improve their overall security and reduce risk by following a Zero Trust model.
- Core principles and benefits: Focus on user identity, continuous verification, and least privilege access. Organizations can greatly reduce the attack surface by doing away with the notion of a trusted network perimeter and implementing stringent access controls instead.
- Deployment approaches: Implementations to secure remote connections and compliance of the enterprise through SDPs, NAC or a more layered form that integrates with other network security solutions.
- Design & Rare-to-Find practices: One of the recommended security measures is multi-factor authentication (MFA) to secure access in some cases.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
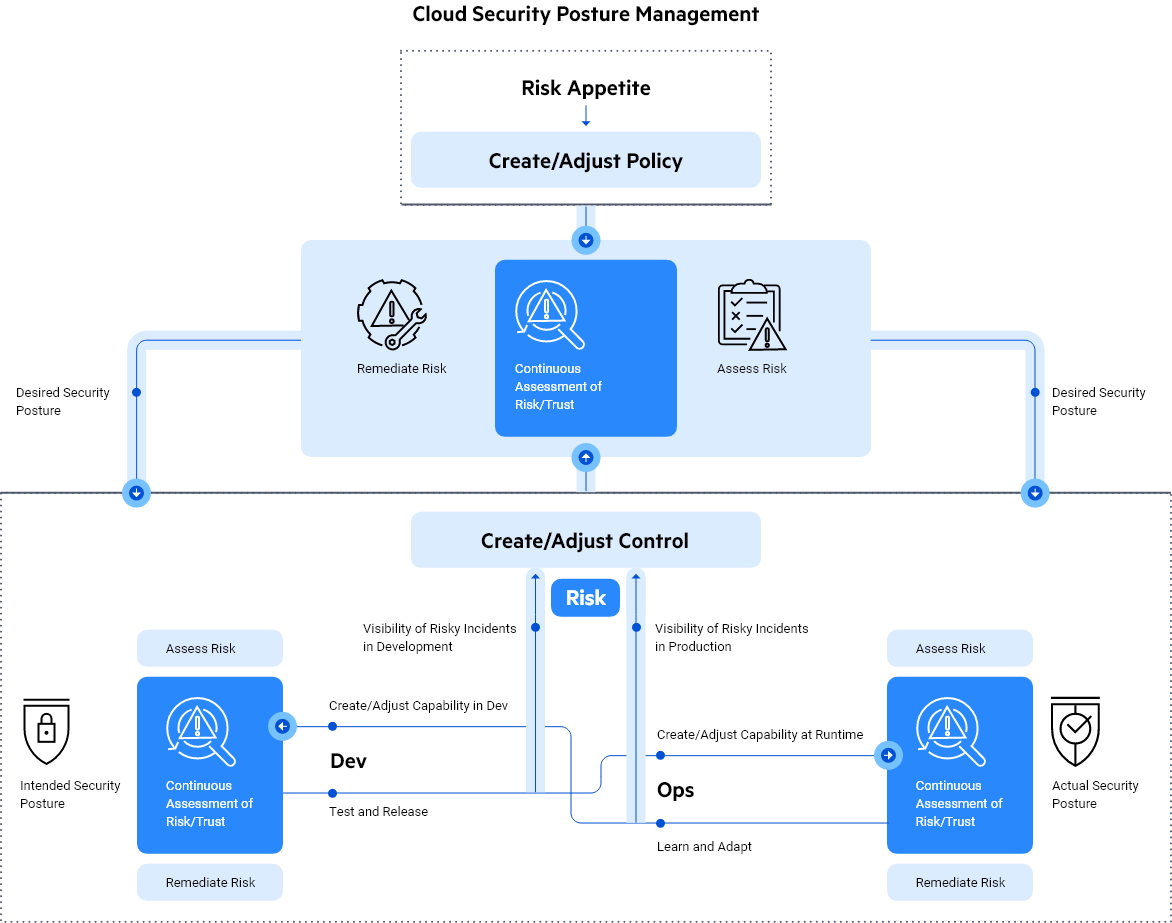
Effective risk management requires maintaining visibility and control over cloud resources. The need for a cloud-agnostic configuration and vulnerability/attack surface management solution has at its roots ion a comprehensive hybrid-cloud security strategy of which Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is an integral part. Cloud security posture management (CSPM) is a set of tools that allows you to monitor and evaluate all your cloud resources for potential vulnerabilities or misconfigurations.
CSPM enables Organisations to have a complete view of their security posture by allowing visibility on cloud resources. It helps detect vulnerabilities, non- compliant configurations and potential threats. Automation is prominent in many CSPM solutions, which can help to speed up the remediation process and mitigate human error.
- Visibility and control are crucial: Gain complete visibility over cloud assets, configurations, vulnerabilities to detect risks before they become issues.
- Features: Inventory management, configuration assessment, compliance monitoring,, risk assessments and remediation guidance.
- Packaging: Leveraging existing security tools to improve overall security posture through data sharing and automation (SIEM, SOAR & IAM)
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs)
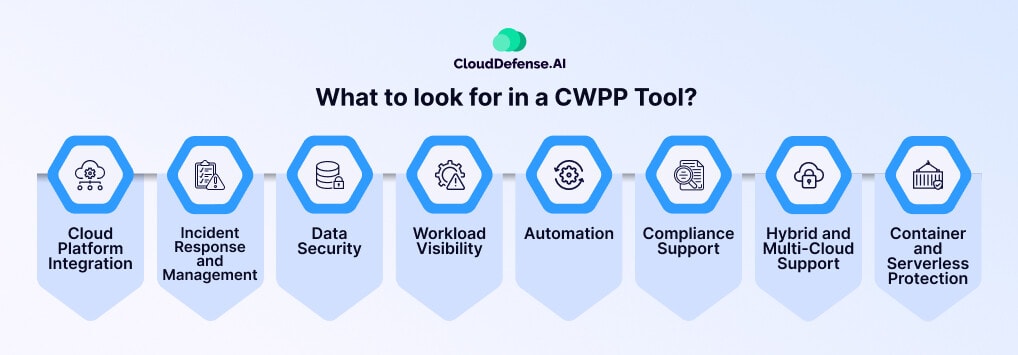
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs) are critical tools for protecting contemporary cloud infrastructures. The comprehensive security solutions secure workloads of form factors such as containers, virtual machines and serverless functions across public cloud (aws / azure), private clouds & hybrid deployments.
- Workload security: Any and every cloud: Including container protection, virtual machine protection, serverless functions from AWS Lambdasand Microsoft Azure Functions.
- Key capabilities and benefits: Runtime application self-protection, vulnerability management, threat detection and response, and compliance enforcement.
- Integration with existing security infrastructure: Enhancing overall security posture and streamlining operations through integration with network security, IAM, and SIEM solutions.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
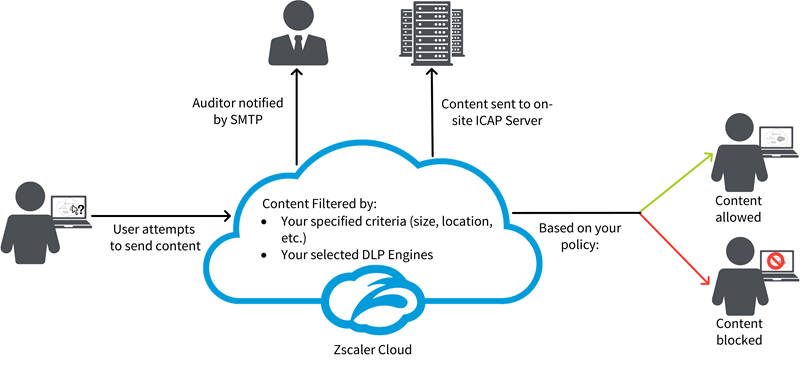
Protecting sensitive data is paramount in hybrid cloud environments.
- Safeguarding sensitive data: Identifying, classifying, and protecting critical information throughout its lifecycle.
- DLP technologies and techniques: Data discovery, classification, monitoring, and prevention using advanced analytics and machine learning.
- Best practices for implementation: Balancing security with user productivity, implementing DLP across the entire data lifecycle, and providing ongoing training and awareness.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Controlling access to resources is fundamental to security.
- Controlling access to resources: Implementing robust authentication, authorization, and single sign-on (SSO) to manage user identities and access privileges.
- IAM best practices: Enforcing strong password policies, utilizing multi-factor authentication, and implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to minimize access privileges.
- Identity governance and administration: Managing user identities and access privileges effectively through lifecycle management, provisioning, and de-provisioning processes.
By understanding and implementing these core solutions, organizations can significantly enhance their hybrid cloud security posture.
Implementing a Comprehensive Security Strategy
To effectively protect your hybrid cloud environment, a holistic approach is essential. By combining the core security solutions with strategic implementation, organizations can build a robust defense against threats.
Hybrid Cloud Environments Security Automation and Orchestration
- Automating repetitive tasks: Streamlining processes such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, incident response, and log analysis to improve efficiency and reduce human error.
- Integrating security tools: Creating efficient workflows and improving response times by connecting security solutions (SIEM, SOAR, IAM, DLP, etc.) into a cohesive security operations center (SOC).
- Orchestrating incident response: Automating actions based on predefined playbooks to accelerate incident handling, minimize damage, and facilitate collaboration between security teams. Consider using workflow automation tools to streamline incident response processes.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
- Real-time visibility: Utilizing security information and event management (SIEM) and log analysis to track system activity, identify anomalies, and detect potential threats in real-time.
- Threat intelligence integration: Staying informed about emerging threats through threat intelligence feeds, analyzing threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), and incorporating this information into security operations.
- Security analytics: Applying advanced analytics and machine learning to detect suspicious patterns, prioritize alerts, and predict potential attacks. Consider using user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to identify anomalous activities.
Security Awareness Training
- Educating employees: Building a security-conscious culture through comprehensive training programs covering topics such as phishing, social engineering, data handling, and incident reporting.
- Phishing simulations: Identifying vulnerabilities in the workforce through simulated attacks to improve user awareness and response capabilities.
- Best practices for handling sensitive information: Empowering teams to protect data through clear guidelines, data classification training, and secure data handling procedures.
Security Assessments and Audits
Regularly evaluating and refining a hybrid cloud environment’s security posture is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring ongoing protection.
Assessing and Auditing Hybrid Cloud Security
- Vulnerability assessments: Identifying potential weaknesses in hardware, software, and network infrastructure to prevent exploitation.
- Penetration testing: Simulating cyberattacks to uncover vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of security controls.
- Compliance audits: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS) and internal security policies.
- Risk assessments: Evaluating potential threats and their impact on the organization to prioritize security efforts.
Identifying and Addressing Security Gaps
- Gap analysis: Comparing the current security posture to industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
- Prioritization: Focusing on critical vulnerabilities and implementing remediation plans based on risk assessment.
- Continuous monitoring: Using security information and event management (SIEM) tools to track system activity and identify emerging threats.
Fostering a Culture of Security
- Security awareness training: Educating employees about security best practices and the importance of protecting sensitive data.
- Incident response planning: Developing and testing incident response plans to minimize the impact of security breaches.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly reviewing and updating security policies, procedures, and technologies based on assessment findings and emerging threats.
By implementing a robust security assessment and audit program, organizations can strengthen their hybrid cloud security posture, protect sensitive data, and build resilience against cyberattacks.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Hybrid cloud environments present unique challenges for various industries due to specific regulatory requirements and data sensitivity.

Hybrid Cloud Security in Regulated Industries
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and government face stringent regulations and data protection mandates.
- Healthcare: Adhering to HIPAA and other regulations while managing patient data in hybrid environments requires robust security measures.
- Finance: Protecting sensitive financial information necessitates compliance with standards like PCI DSS and GDPR.
- Government: Ensuring data sovereignty, security, and compliance with government regulations is paramount.
Cloud Security Compliance
Remaining compliant in an industry of compliancy standards is key to trust and penalty avoidance.
Regulatory frameworks: Comprehension and compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS or industry standards.
Risk assessment: Discovering and lessening the compliance risk of running in hybrid cloud-mode.
Monitoring and Audits: Continuous monitoring must be implemented along with regular audits to ensure continued compliance.
These are just some of the industry-specific concerns and organizations that address these risk factors can manage their hybrid cloud security risks effectively to build trust among customers, partners, stakeholders.
A-Dev Enables to Overcome Hybrid Cloud Challenges
BrainKey, a healthcare platform specializing in 3D brain visualizations, faced significant obstacles in its cloud infrastructure. As the company had to meet ample deadlines, and related requirements of a compliance regime (like amendments in minutes etc.), it was under tremendous pressure due this status change; such where AWS Cloud stand-in service tier while notifying the customer for suitable processing; they needed top notch Data Migration from our software on an impressive escalating data volumes shortly effects.
BrainKey partnered up with A-Dev for the cloud migration and optimization aspects of these challenges. We then devised a hybrid cloud approach riding on Azure with Kubernetes for container orchestration and Terraform to codify our infrastructure.
Key challenges included:
- Data migration: Transferring substantial volumes of sensitive patient data to the new cloud environment without compromising data integrity.
- Performance optimization: Ensuring the platform could handle increasing workloads and deliver seamless user experiences.
- Infrastructure complexity: Managing diverse infrastructure components across multiple cloud platforms.
A-Dev manages and cleans up much of the metadata, making sure that proper log events are created in Node (this was a big one) so you can analytically ask what is being logged. With the help of these state-of-the-art migration tools and techniques, infrastructure optimization and full implementation for data management solutions we migrated an entire platform BrainKey in Azure.
The collaboration between BrainKey and A-Dev resulted in significant improvements in performance, scalability, and overall operational efficiency. This case study underscores the importance of a well-executed hybrid cloud strategy and the value of partnering with experienced cloud migration specialists.
Conclusion
Hybrid Cloud Security Advancement with cloud computing always on the rise, secure hybrid clouds are more important than ever. Enterprises need to take a holistic view of security for their hybrid environment and consider the unique threats when private and public clouds are integrated. Applying the security best practices mentioned in this guide — including embracing a zero trust model, encrypting data and running periodic assessment of security programs can help businesses secure their digital assets while ensuring strong cyber posture across environments.
It is important to incorporate unified security policies into the different cloud service providers when multiple clouds are utilized from same organization. In addition to protecting data and maintaining customer trust, this approach enables businesses to secure their hybrid cloud environments while ensuring that they are resilient and compliant with industry regulations.





