FERPA (Family Education Rights and Privacy Act) is a federal law that protects students’ education records. Even though they may look right away the same, both of them have a different scope and usage.
They say FERPA is often confused with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, or HIPPA, because both deal in personal privacy. But it is important for educational institutions, health care providers, and you to understand the nuances and key differences between them so that rights are protected through proper compliance efforts.
This post takes a closer look at the distinctions between HIPAA and FERPA, examines where they overlap in education environments, and offers recommendations for how to safeguard your data while complying with both laws.
What are FERPA and HIPAA?
In the United States, FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) are federal laws that respectively protect education records as part of their privacy rights as health-related data.
- FERPA applies to student education records, defined as “records that are directly related to a student and maintained by an educational agency or institution or by a party acting for the agency or institution.” That can be grades, test scores, a discipline record, and so on.
- HIPAA applies to protected health information (PHI), which is any information that can be used to identify an individual and relates to their past, present, or future health condition. This is a wide-ranging set of information, which may include medical records, billing and insurance claims.
Do School Nurses Follow HIPAA or FERPA?
School nurses must follow not only FERPA but also HIPAA as they manage both educational records and medical information. Thus, they are subject to the privacy and security mandates set forth by both laws when handling student information.
Does HIPAA Apply to Educational Settings?
HIPAA applies to educational settings when they are acting as healthcare providers. This means that schools must comply with HIPAA if they operate school clinics, health centers, or other entities that provide medical services.
What is the HIPAA Equivalent for Schools?
There is no direct equivalent to HIPAA for schools. But schools face several other federal and state laws that aim to shield student dataprivacy, most notably FERPA.
FERPA vs. HIPAA: Key Similarities and Differences
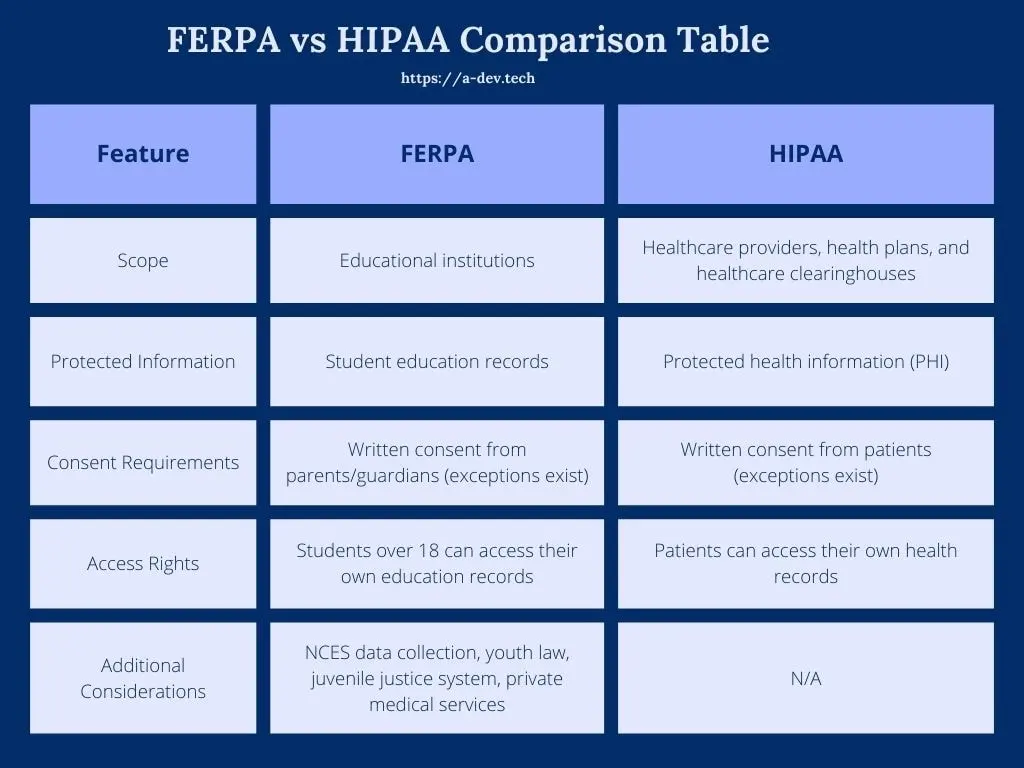
HIPAA and FERPA provide protections for personal information privacy, but they have different scopes or application areas. Let us understand their major similarities and differences.
Similarities:
- Federal Laws: FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) are both federal regulations, which means you must comply with them if you fall under their scope of regulation.
- Data Protection: they mandate that covered entities have measures in place to ensure the security of information they are processing and provide individuals with specific rights as regards their data.
Differences:
- Scope: FERPA applies to anyone who works in the fields of elementary, secondary, college and university settings. Unlike the DPA, HIPAA is concerned with healthcare entities (i.e., providers, health plans, and clearinghouses respectively).
- Confidential Information: FERPA protects education records, any information related to a student’s educational experience kept by the institution. On the other hand, HIPAA secures protected health information (PHI), defined as any information tying an individual to their past, present or future physical or mental health condition.
- Consent Requirements: FERPA typically mandates written consent from a parent or legal guardian to disclose student records, with exceptions. While HIPAA generally requires patients to provide specific, written consent for the vast majority of PHI disclosures, there are exceptions (e.g., treatment, payment or health-care operations).
- Access Rights: Students over 18 have the right to access their own education records under FERPA. Similarly, HIPAA grants patients the right to access their own health records.
Additional Considerations:
- Subject to certain conditions, the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) can also collect or release student data for research purposes without written consent.
- FERPA is classified as youth law and HIPAA centers around healthcare.
- Under some circumstances, information in a student’s education record may be released to juvenile justice agencies pursuant to FERPA.
- If a school provides private medical services (for example, a clinic), HIPAA would apply to the medical records maintained there.
Compliance and Data Protection

Source: Freepik
Why FERPA and HIPAA Compliance is Vital
A-Dev, as a cloud migration and DevOps service provider must keep the security of your sensitive data and privacy. This includes following all federal regulations, such as FERPA and HIPAA.
Key Strategies for Proactive Data Protection
- Implement Strong Security Measures:
- Encryption: data should be encrypted both in rest and in transmission, to prevent them from been accessed by unauthorized users.
- Access Controls: Ensure fine-grained access controls are in place to restrict both the people who can and actions they can undertake in regards to sensitive data.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits will allow you to find and fix vulnerabilities.
- Patch Management: Regularly update systems and software with the latest security patches.
- Encryption: data should be encrypted both in rest and in transmission, to prevent them from been accessed by unauthorized users.
- Train Staff on Data Privacy:
- Awareness Training: Make sure that all you employees undergo in depth training on the relevancy of data privacy and security.
- Best Practices: Train your team on good habits for sensitive data processing, storage, and destruction.
- Incident Response: Ensure staff understands how to respond in cases of data breach and other security incidents.
- Awareness Training: Make sure that all you employees undergo in depth training on the relevancy of data privacy and security.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments:
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Conduct periodic assessments of your systems, processes and search for potential threats in security.
- Prioritize Risks: Rank risks based upon probability and impact.
- Implement Mitigations: What can be done to reduce the likelihood of those risks you identified during your data assessment?
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Conduct periodic assessments of your systems, processes and search for potential threats in security.
- Keep Abreast of Regulatory Changes
- Monitor Regulations: Keep track of changes to FERPA and HIPAA regulations.
- Update Policies and Procedures: Make sure your policies align with the latest legal requirements.
- Monitor Regulations: Keep track of changes to FERPA and HIPAA regulations.
Enhancing Security with Software Solutions
- Data Encryption: Protect both in-flight and at-rest with encryption tools.
- Access Controls: Use access control so only those of a certain level can enter and manipulate sensitive information.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools to prevent unauthorized data transfers and leaks.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Implement a SIEM solution to track network-activity and identify security-breach in real time.
A-Dev is committed to providing you with the highest level of data security and compliance. We have implemented robust security measures and processes to ensure that your data is protected.
If you follow these methods and take advantage of the newest security tools available, you will be able to secure your data and stay compliant with FERPA and HIPAA.
The Intersection of FERPA and HIPAA
- How do FERPA and HIPAA intersect in educational settings?
Since schools offer healthcare they are covered by both of these laws. These scenarios coincide with those defined in HIPAA AND FERPA, and schools must adhere to both standards. - What are the key considerations for schools dealing with both FERPA and HIPAA?
The Department of Education and HHS have jointly issued guidance that schools can turn to. They may also be required to have written permission from a parent or legal guardian in order to disclose student health status to healthcare providers.
Additional Questions
- Can parents access their child’s medical records maintained by the school?
Even though parents usually have the right to access their child’s health-related records, procedures for gaining this access might differ according to individual state or local laws. - Can schools disclose student health records to law enforcement?
Under limited circumstances (for example, if there is a safety issue), schools can share student medical records with law enforcement. However there are some strict regulations on it.
Conclusion
The HIPAA and FERPA are common laws that protect personal information. While there is some overlap in their contents, they are used in different contexts as dictated by where knowledge of English each student has. Educational institutions and healthcare providers need to understand these differences to be compliant with the law, thereby protecting the privacy of their students and patients.
Organizations can protect data in advance and remain fully compliant with both HIPAA and FERPA through the implementation of robust security measures, staff training, and monitoring changes in regulations.






